Types of Network Architecture
There are several types of network architectures that can be used to design and implement a computer network.
a. Client and Server Network
b. Peer to Peer (P2P) Network
c. Point-to-Point Network
Some of the most common types of network architectures include:
a. Client and Server Network
b. Peer to Peer (P2P) Network
A peer-to-peer (P2P) network is a type of network architecture in which a group of computers are all equal in terms of their abilities and responsibilities. In a P2P network, there is no central server that stores and manages data and resources. Instead, each computer on the network can act as both a client and a server, and they can share resources with one another directly.
P2P networks are often used for file sharing, as they allow users to share files directly with one another without the need for a central server. They can also be used for other types of resource sharing, such as sharing access to printers or other devices.
One advantage of P2P networks is that they are often more resilient and scalable than client-server networks, as there is no single point of failure. However, they can also be more vulnerable to security risks, as there is no central authority that controls access to resources.
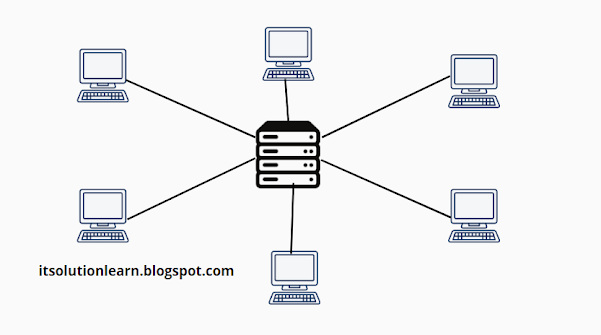
c. Point-to-Point Network
A point-to-point network, also known as a point-to-point link, is a type of network connection that allows two devices to communicate with each other directly over a dedicated link. This type of connection is used to establish a direct communication path between two devices, without the need for intermediaries such as routers or switches.
Point-to-point networks are often used to connect two devices that are located far apart from one another, such as in different buildings or across long distances. They can be used to connect devices within a single organization, or to connect two different organizations.
Point-to-point networks can be established using a variety of technologies, including fiber optic cables, copper cables, and wireless links. They are often used in situations where a high-speed, reliable connection is needed, such as for transmitting large amounts of data or for supporting real-time applications.
Fig 3 shows point to point network.
Fig 3 Point-To-Point Network




0 Comments